Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Akamatsu, Ken
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1179 - 1183, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.28(Chemistry, Physical)An ionizing radiation-sensitive liposome has been developed aiming for irradiation site-specific controlled release of an anticancer agent from liposomes accumulated at tumor. As the first step of the study, X-ray-sensitive liposome has been constructed, consisting of an unsaturated phosphatidyl choline (PC), a saturated PC, and cholesterol. The radiation sensitivity was estimated by measuring release rate of a fluorophore, calcein, through the lipid bilayer. As a result, the following characteristics of X-ray-sensitive liposomes were discovered: (1) A PC with bis-allylic hydrogen is an essential component of unsaturated PC, (2) Dilinoleoyl PC (DLOPC) is the most favorable component of unsaturated PC, (3) A lower dose rate makes the liposome more X-ray-sensitive. In this presentation, we will discuss radiation chemical mechanism of the ionizing radiation-sensitive liposome, and their pharmaceutical applications for radiation therapy such as boron neutron capture therapy.
Sugo, Yumi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sasaki, Yuji; Hirota, Koichi; Kimura, Takaumi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1140 - 1144, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:31 Percentile:87.31(Chemistry, Physical)In the actual partitioning process of HLW, the organic complexing agent will be exposed to  -particles emitted by
-particles emitted by  -decay of the actinides. In this study,
-decay of the actinides. In this study,  -radiolysis of TODGA in
-radiolysis of TODGA in  -dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by the AVF cyclotron or the tandem accelerator in the TIARA facility at JAEA Takasaki. It was found that the radiation chemical yield for the degradation of TODGA by helium ion beam irradiation was less than that by
-dodecane was investigated by the irradiation with helium ion beam accelerated by the AVF cyclotron or the tandem accelerator in the TIARA facility at JAEA Takasaki. It was found that the radiation chemical yield for the degradation of TODGA by helium ion beam irradiation was less than that by  -rays irradiation. It was also observed the radiation chemical yield gradually increased with the incident energy of helium ions. These results indicate that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA is reduced by high LET radiations such as
-rays irradiation. It was also observed the radiation chemical yield gradually increased with the incident energy of helium ions. These results indicate that the radiolytic degradation of TODGA is reduced by high LET radiations such as  -particles. Because the radical cations of
-particles. Because the radical cations of  -dodecane, which contribute to the charge transfer reaction described above, decrease by recombination in track.
-dodecane, which contribute to the charge transfer reaction described above, decrease by recombination in track.
Hatano, Yoshihiko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1021 - 1025, 2009/12
From our recent surveys of the research fields of charged particle and photon interactions with matter, we have obtained the important information on future problems needing more work in these research fields and also on ideas how to activate further scientifically radiation chemistry. The important points to be discussed in this talk, therefore, from the entitled views are, (1) Important core-parts of radiation chemistry should be activated further more, which will not result in producing the community isolated from others. (2) Research fields of physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, and technology in radiation research should interact more scientifically among them with each other. (3) Basic research should interact more with applied research to create overlapped specific areas between them. (4) Interface research fields with radiation chemistry should be produced more with mutually common viewpoints between the two of the ionization and excitation of molecules in matter.
Onoda, Shinobu; Hirao, Toshio; Oshima, Takeshi; Ito, Hisayoshi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1116 - 1119, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.28(Chemistry, Physical)The effects of radial ion track distribution on the unexpected noise (transient current) in semiconductors by a high energy heavy ion strike have been studied. The measured transient currents were compared with the numerically observed one, which was calculated with the wide variety of ion track radii. In the case of low energy (several MeVs) ion, the calculated transient currents were independent of the radial track distribution. However, in the case of high energy (several hundreds of MeVs) ion, the transient currents strongly depend on the radial track distribution. This difference is interpreted in terms of the carrier concentration at the core of track, resulting in the extremely different carrier mobility. When the radius of ion track used in numerical simulator was shorter than, or equivalent to, the penumbra radius, the reasonable agreement was found between experimental and calculated transient currents.
 -edge
-edgeUkai, Masatoshi*; Yokoya, Akinari; Nonaka, Yusuke*; Fujii, Kentaro; Saito, Yuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1202 - 1206, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.97(Chemistry, Physical)To substantiate the hydrated structure of DNA from the view point of the electronic properties, we developed a new spectroscopic technique of photoelectrons ejected from solutions dissolving biological molecules using soft X-ray synchrotron radiation in combination with liquid jet in vacuum. The experiments are carried out at the BL23SU in SPring-8, Japan. The liquid sample is maintained in the form of continuous micro-beam ( = 20
= 20  m) in vacuum and is intersected by a well focused nearly micro-beam of synchrotron-radiation of less than 50
m) in vacuum and is intersected by a well focused nearly micro-beam of synchrotron-radiation of less than 50  m. In this paper, we present (1) the partial yields of photoelectrons for liquid water molecules and oxygen Auger electron spectra in the energy range around the oxygen K-edge, and (2) the total photoelectron yields for DNA nucleotides (AMP, CMP, and GMP) in water solutions near nitrogen K-edge, which correspond to the X-ray absorption spectra (XANES).
m. In this paper, we present (1) the partial yields of photoelectrons for liquid water molecules and oxygen Auger electron spectra in the energy range around the oxygen K-edge, and (2) the total photoelectron yields for DNA nucleotides (AMP, CMP, and GMP) in water solutions near nitrogen K-edge, which correspond to the X-ray absorption spectra (XANES).
Kondo, Takafumi*; Asano, Akira*; Yang, J.*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Takahashi, Kenji*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kato, Ryuji*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1157 - 1160, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:28 Percentile:85.84(Chemistry, Physical)Spectrum and kinetic behavior of solvated electrons (e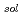
 ) in alkyl ammonium ionic liquids (ILs),
) in alkyl ammonium ionic liquids (ILs),  DEMMA-TFSI, DEMMA-BF4, TMPA-TFSI, PP13-TFSI, P13-TFSI and P14-TFSI were investigated by pulse radiolysis method. The e
DEMMA-TFSI, DEMMA-BF4, TMPA-TFSI, PP13-TFSI, P13-TFSI and P14-TFSI were investigated by pulse radiolysis method. The e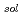
 in the ILs have same absorption peak at 1100 nm with a molar absorption coefficient of 1.5-2.3
in the ILs have same absorption peak at 1100 nm with a molar absorption coefficient of 1.5-2.3 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol cm
cm . The reaction rate constant of e
. The reaction rate constant of e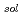
 with Pyrene (Py) was 1.5-3.5
with Pyrene (Py) was 1.5-3.5 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s . These values were about one order of magnitude higher than that of diffusion controlled limit, which was calculated from measured viscosity. The dry electron (e
. These values were about one order of magnitude higher than that of diffusion controlled limit, which was calculated from measured viscosity. The dry electron (e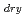
 ) reacts with Py, and its rate constant in DEMMA-TFSI was 7.9
) reacts with Py, and its rate constant in DEMMA-TFSI was 7.9 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s , three orders of magnitude higher than that of the e
, three orders of magnitude higher than that of the e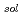
 reactions.
reactions.
Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Hata, Kuniki; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari; Hatano, Yoshihiko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 78(12), p.1192 - 1197, 2009/12
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:87.31(Chemistry, Physical)Yamaguchi, Makoto; Naito, Morimasa; Yui, Mikazu
no journal, ,
To assess the effect of alpha-radiolysis of groundwater on the surface of the radioactive waste in the HLW disposal, helium ion beam irradiation of aqueous solutions were performed containing bicarbonate, which is the major solute in groundwater. Samples were irradiated with 20 MeV  He
He ion beam from AVF cyclotron in TIARA, and hydrogen peroxide was analyzed. Hydrogen peroxide concentration increased linearly with accumulated dose, and its accumulation rate decreased by increasing solute concentration. This effect of bicarbonate ion shows the same trend as observed in the previous homogeneous kinetic model calculations.
ion beam from AVF cyclotron in TIARA, and hydrogen peroxide was analyzed. Hydrogen peroxide concentration increased linearly with accumulated dose, and its accumulation rate decreased by increasing solute concentration. This effect of bicarbonate ion shows the same trend as observed in the previous homogeneous kinetic model calculations.
Yoshida, Masaru; Kimura, Yosuke; Chen, J.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
The development of polymer electrolyte fuel cell membranes with a higher proton conduction pathway in the thickness direction of the film is advanced by introduction of graft chains in the latent tracks zone formed along the swift heavy ion with both the UV-grafting and the  -grafting. In this study, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film was irradiated with ion species of 450 MeV
-grafting. In this study, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) film was irradiated with ion species of 450 MeV  Xe
Xe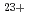 and 56 MeV
and 56 MeV  N
N , to obtain the iPTFE film. The iPTFE proton-conducting membranes with an ion-exchange capacity of 0.4-0.6 mmol/g were prepared in the UV- and
, to obtain the iPTFE film. The iPTFE proton-conducting membranes with an ion-exchange capacity of 0.4-0.6 mmol/g were prepared in the UV- and  -grafting methods. The proton conductivity (
-grafting methods. The proton conductivity ( ) in the thickness direction of the PTFE-specimen without ion-beam irradiation was obtained to be 0.03 S/cm. In contrast to this, the
) in the thickness direction of the PTFE-specimen without ion-beam irradiation was obtained to be 0.03 S/cm. In contrast to this, the  value of the iPTFE proton-conducting membranes reached both up to 0.08 S/cm in two methods, when the Xe ions with a fluence of 3
value of the iPTFE proton-conducting membranes reached both up to 0.08 S/cm in two methods, when the Xe ions with a fluence of 3 10
10 ions/cm
ions/cm were irradiated.
were irradiated.
Chen, J.; Zhai, M.; Asano, Masaharu; Maekawa, Yasunari; Yoshida, Masaru
no journal, ,
Polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells are very promising as power sources for automotive applications, where stability and durability at a high temperature and low humidity are demanded. The currently used expensive Nafion membranes are not appropriated for application in high temperature fuel cells. For this reason, an inexpensive polyetheretherketone (PEEK)-based polymer electrolyte membrane (ssPEEK) was prepared by successive two-step grafting of divinylbenzene and ethyl styrenesulfonate onto PEEK film, followed by hydrolysis of the ETSS graft chains to form styrenesulfonate graft chains. The results of the fuel cell test showed that ssPEEK has a performance comparable to Nafion at lower temperature and higher humidify, and much better performance at higher temperature and lower humidify. In addition, at the latter, the ssPEEK-based cell could be operated with stable performance for more than 250 h without any substantial voltage drop, whereas the voltage of the Nafion-based cell continuously dropped over the same duration.
 irradiation
irradiationHiroki, Akihiro; Tran Thu, H.*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Yagi, Toshiaki*; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
In this study, we have investigated the spectral of the X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) of DNA caused by exposure to monochromatic soft X-rays. We used a calf thymus DNA thin film as a sample and observed nitrogen K-shell and oxygen K-shell XANES spectral changes. The typical monochromatic soft X-ray energies used for the irradiation (395, 408, 528, and 538 eV) were obtained from SPring-8, BL23SU. These energies correspond to just below nitrogen K-shell, just above nitrogen K-shell, just below oxygen K-shell, and just above oxygen K-shell, respectively. The obtained results indicate that carbonyl groups may be produced in the sample. In particular, the production of a propenal group (O=C-C=C) by oxygen ionization is expected. We will discuss the site selective damage induction in DNA using highly monochromatized synchrotron soft X-rays.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji
no journal, ,
Radiation induced reduction of Cr O
O
 and Ce
and Ce in acidic aqueous solutions of colloidal silica was studied by
in acidic aqueous solutions of colloidal silica was studied by  -radiolysis experiment. Based on the results the effect of silica on radiolysis of water was discussed. Reduction yield of Cr
-radiolysis experiment. Based on the results the effect of silica on radiolysis of water was discussed. Reduction yield of Cr O
O
 was measured to slightly decrease with the increasing amount of colloidal silica in the presence of
was measured to slightly decrease with the increasing amount of colloidal silica in the presence of 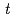 -butanol. Similar decrease in reduction yield of Ce
-butanol. Similar decrease in reduction yield of Ce was observed in the presence of formic acid. These result indicate that generation of reactive species per unit energy absorbed by silica particle is slightly less efficient than that by water, although energy absorption coefficient of silica is higher than that of water because of higher electron density. Therefore it is difficult to attribute the effect of oxides coexistence to increase in primary yields of reactive species. Study on the chemical process in the presence of oxides is necessary.
was observed in the presence of formic acid. These result indicate that generation of reactive species per unit energy absorbed by silica particle is slightly less efficient than that by water, although energy absorption coefficient of silica is higher than that of water because of higher electron density. Therefore it is difficult to attribute the effect of oxides coexistence to increase in primary yields of reactive species. Study on the chemical process in the presence of oxides is necessary.
Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Matsumoto, Kanae*; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
The quantity of OH radicals, produced in humid N under 1-MeV EB irradiation, was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO
under 1-MeV EB irradiation, was indirectly determined using an index of oxidation of CO to CO , which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. The concentration of water vapor to fully react with the positive ions/excited species was examined under different initial concentrations of water vapor. The concentration of CO to scavenge completely the produced OH radicals was also measured under different initial CO concentrations. As a result, such concentrations of water vapor and CO were higher than 6,000 and 2,000 ppmv, respectively. The experiment using this condition of CO and water vapor demonstrated that the concentration of CO
, which has been used in atmospheric chemistry. The concentration of water vapor to fully react with the positive ions/excited species was examined under different initial concentrations of water vapor. The concentration of CO to scavenge completely the produced OH radicals was also measured under different initial CO concentrations. As a result, such concentrations of water vapor and CO were higher than 6,000 and 2,000 ppmv, respectively. The experiment using this condition of CO and water vapor demonstrated that the concentration of CO , produced from reaction of CO with OH radicals, lineally increased with doses of 0-10 kGy and the G(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
, produced from reaction of CO with OH radicals, lineally increased with doses of 0-10 kGy and the G(OH) was estimated as 4.90.
Maeyama, Takuya*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Baldacchino, G.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Muroya, Yusa*; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Detailed mechanism in which effectiveness of heavy ions in cancer therapy are derived from is not known well. It is inevitably important to examine water radiolysis with high-energy heavy ions because water is main component of human body. Among several water decomposition products, OH is known to be most responsible for radiation induced cell death in indirect actions. OH yield has been reported for heavy-ion irradiations in several works employing absorption analyses. With increasing LET, OH yield decreases monotonically (at least up to several hundred eV per nm). Then, more sensitive way to determine OH yield is preferable for higher LET region. In this work, a fluorescent probe, coumarin-3-carboxylic acid, was applied for OH-yield determination as a sensitive way of quantification of OH radical production. Especially, OH yield near the Bragg peaks was discussed.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Maeyama, Takuya*; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*
no journal, ,
Water radiolysis with heavy ions, from helium to iron ions, of very high energies up to 28 GeV (namely several hundred MeV per nucleon) has been studied in this work. Simulations based on diffusion kinetic model were performed to examine correlation between initial track structures at the beginning of the chemical stage, 10-12 s, and primary yields as well as to estimate the validity of classical track structure model for highly energetic heavy ions.
Hirota, Koichi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Hakoda, Teruyuki; Shimada, Akihiko; Kimura, Atsushi
no journal, ,
Parajuli, D.; Hirota, Koichi
no journal, ,
Zhai, M.; Hasegawa, Shin; Chen, J.; Maekawa, Yasunari
no journal, ,
To develop a highly chemicallly stable polymer electrolyte membrane for appilcation in a direct methanol fuel cell, a fluorinated monomer, Bromotetrafluoroethyl trifluorovinyl ether (BrTFF), was grafted firstly into poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE) membrane by irradiation. Further, a new-type polymer electrolyte membrane was synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization of styrene into ETFE-graft-polyBrTFF membrane followed by sulfonation. The bromine groups in ETFE-graft-polyBrTFF membrane functioned as initiators, and a Cu-based catalytic system of Cu(I)Br and bipyridyl (bpy) was empolyed for the ATRP. It was found that styrene was grafted homogeneously into ETFE-graft-polyBrTFF membrane and the prepared polymer electrolyte membrane have higher ion exchange capacity (IEC) and proton conductivity than that of normal ETFE-g-PSSA membrane.
Kumagai, Yuta; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Reactions of colloidal silica with OH radical and hydrated electron were studied by pulse radiolysis technique. Colloidal silica samples were prepared by hydrolysis of TEOS (Si(OC H
H )
) ) and solutions containing colloidal silica were compared to control solutions containing the filtrate of the colloidal silica samples, in order to avoid the effect of stabilizer and other impurities. For hydrated electron, transient light absorption was measured directly. Decay kinetics of hydrated electron were observed to be almost identical in the presence and absence of colloidal silica. On the other hand, for OH radical, absorption of carbonate radical formed by the reaction of OH radical with bicarbonate ion was measured to decrease in the presence of colloidal silica. This result indicates a competitive reaction between colloidal silica and bicarbonate ion with OH radical, and the reactivity of colloidal silica toward OH radical.
) and solutions containing colloidal silica were compared to control solutions containing the filtrate of the colloidal silica samples, in order to avoid the effect of stabilizer and other impurities. For hydrated electron, transient light absorption was measured directly. Decay kinetics of hydrated electron were observed to be almost identical in the presence and absence of colloidal silica. On the other hand, for OH radical, absorption of carbonate radical formed by the reaction of OH radical with bicarbonate ion was measured to decrease in the presence of colloidal silica. This result indicates a competitive reaction between colloidal silica and bicarbonate ion with OH radical, and the reactivity of colloidal silica toward OH radical.